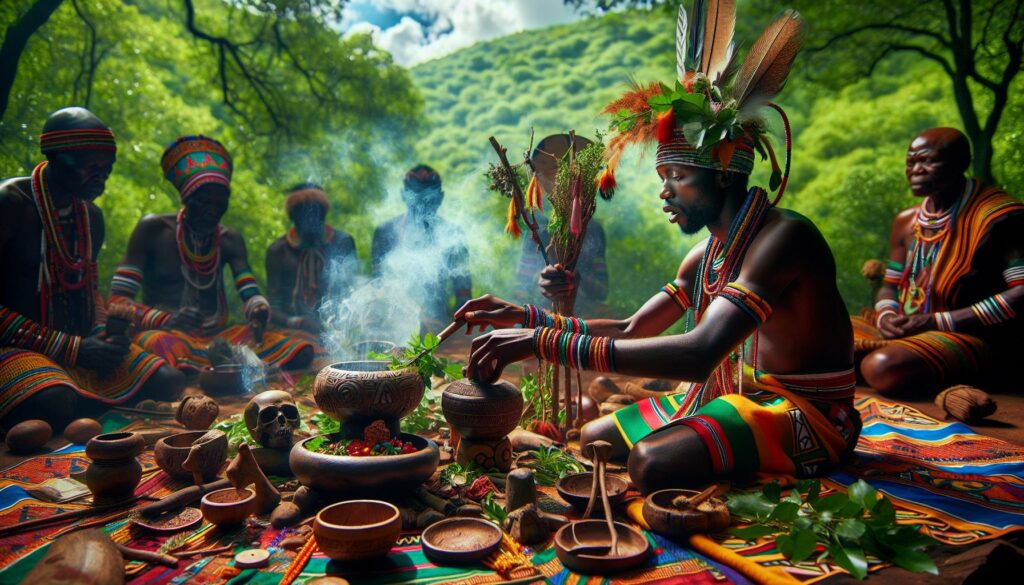
Gizavuhovhulo, a traditional healing practice deeply rooted in South African culture, continues to play a vital role in modern healthcare. This ancient art combines spiritual rituals, herbal remedies and ancestral wisdom to treat both physical and psychological ailments within local communities. The practice has gained recognition beyond its traditional boundaries as researchers explore its potential contributions to contemporary medicine. While Western medical professionals once dismissed gizavuhovhulo, they’re now studying its unique approach to holistic healing and the effectiveness of its natural treatments. The integration of these time-honored methods with modern medical practices represents a growing trend in global healthcare solutions.
Gizavuhovhulo
Gizavuhovhulo is a traditional healing system practiced by the Venda people of South Africa’s Limpopo province. The practice integrates spiritual ceremonies herbal medicine diagnostics ancestral communication to restore physical mental emotional balance in patients. Key components of gizavuhovhulo include:-
- Ritual ceremonies performed at sacred sites using traditional instruments drums animal horns
-
- Herbal preparations derived from indigenous plants roots bark leaves
-
- Spiritual consultations with ancestral guides through meditation trance states
-
- Energy cleansing practices using smoke water natural elements
-
- Diagnostic methods combining physical examination spiritual assessment
-
- Physical healing through medicinal herbs mineral compounds animal products
-
- Spiritual healing via ceremonial rituals ancestral communication energy work
-
- Social healing through community involvement counseling support systems
| Treatment Component | Purpose | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Initial consultation | Diagnosis spiritual assessment | 1-2 hours |
| Herbal remedies | Physical symptom treatment | 7-14 days |
| Ritual ceremonies | Spiritual cleansing healing | 3-5 days |
| Follow-up care | Progress monitoring adjustments | Monthly |
-
- Chronic pain ailments including arthritis migraines muscle tension
-
- Mental health issues such as anxiety depression trauma
-
- Digestive disorders respiratory problems skin conditions
-
- Reproductive health concerns fertility issues menstrual disorders
-
- General immune system strengthening energy balancing
Origins and Cultural Significance
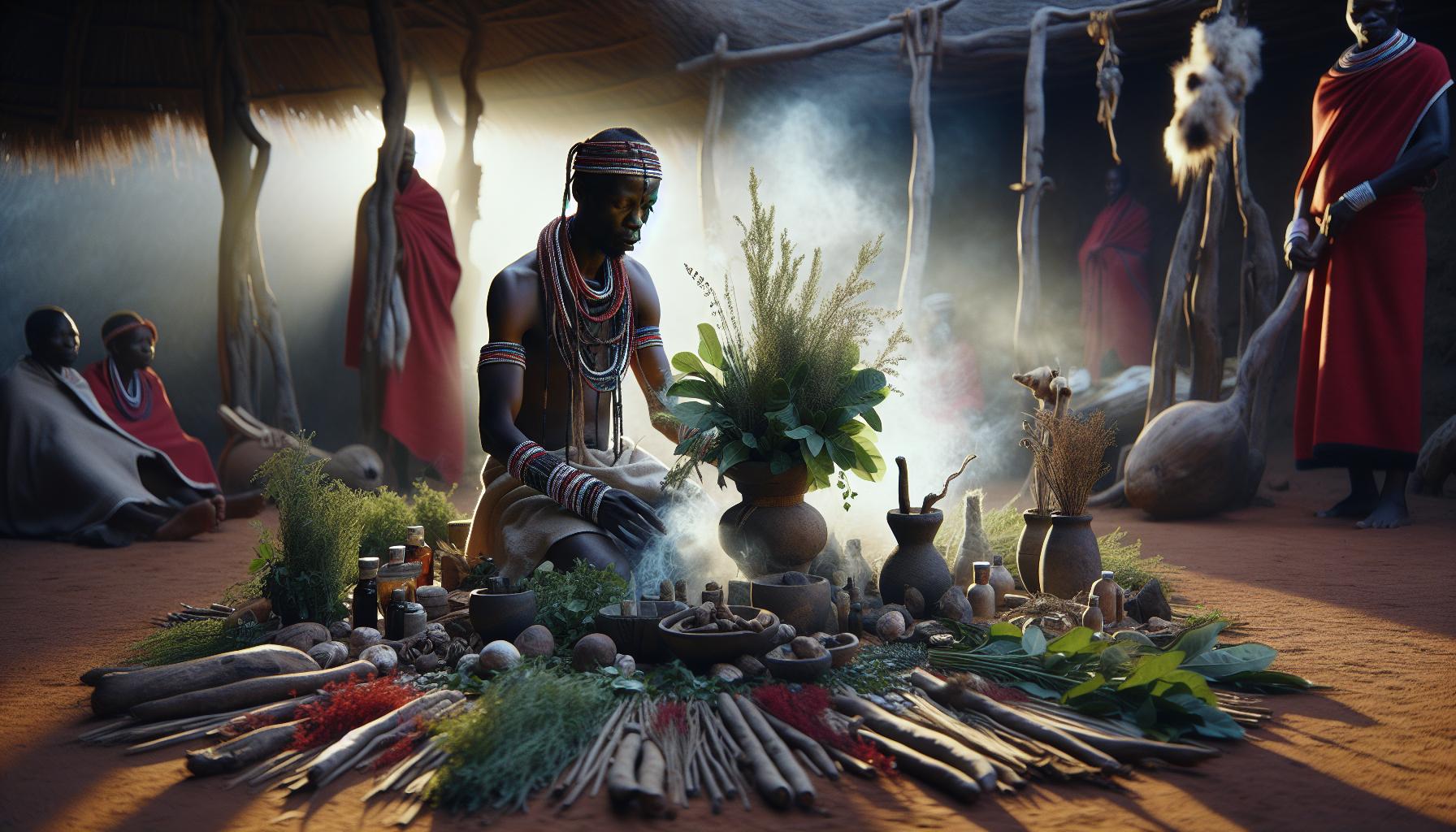

Traditional Uses in African Communities
The Venda people integrate gizavuhovhulo into major life events including:-
- Birth ceremonies to protect newborns through ritual cleansing
-
- Coming-of-age rituals marking transitions into adulthood
-
- Marriage preparations involving spiritual purification
-
- Death rites connecting the living with ancestral spirits
-
- Seasonal agricultural ceremonies promoting abundant harvests
-
- Conflict resolution between families or clans
-
- Environmental conservation guidance
-
- Community healing ceremonies during epidemics
-
- Protection rituals for villages
-
- Spiritual guidance during cultural festivals
Historical Development
The evolution of gizavuhovhulo spans distinct historical periods: Pre-Colonial Era (Before 1652):-
- Establishment of core healing practices
-
- Development of specialized herbal knowledge
-
- Creation of diagnostic methods
-
- Formation of practitioner training systems
| Period | Key Developments |
|---|---|
| 1700s | Underground practice to preserve traditions |
| 1800s | Integration of new medicinal plants |
| 1900s | Adaptation to changing social structures |
-
- Recognition by South African Traditional Health Practitioners Act
-
- Documentation of healing methods by researchers
-
- Integration with modern healthcare systems
-
- Establishment of practitioner associations
Key Components and Materials
Gizavuhovhulo practitioners utilize specific materials and components in their healing practices. These elements combine traditional knowledge with locally sourced materials to create effective healing environments and treatments.Core Elements
-
- Sacred herbs: Indigenous plants like Lippia javanica (fever tea) Artemisia afra (African wormwood) form the foundation of medicinal preparations
-
- Ritual tools: Carved wooden bowls (ndilo) clay pots (khali) calabash containers (mafheko) for storing and preparing medicines
-
- Ceremonial items:
-
- White cloth (mashie) for purification rituals
-
- Sacred stones (thugwa) for diagnostic readings
-
- Animal hide drums (ngoma) for trance ceremonies
-
- Natural elements:
-
- Spring water (madi a mupo) for cleansing
-
- Sacred clay (vumba) for protective applications
-
- Indigenous tree bark for medicinal preparations
-
- Preparation techniques:
-
- Sun-drying of herbs at specific lunar phases
-
- Grinding materials using traditional stone tools
-
- Fermentation of plant mixtures in clay vessels
-
- Storage systems:
-
- Underground storage pits lined with specific tree bark
-
- Elevated wooden platforms for drying materials
-
- Sealed clay containers for preserved medicines
-
- Processing methods:
-
- Cold extraction for delicate plant materials
-
- Hot infusion for bark and root preparations
-
- Smoke curing for preservation of ceremonial items
-
- Sacred space construction:
-
- Circular healing huts (pfamo) built with specific wood types
-
- Designated preparation areas aligned with cardinal directions
-
- Ventilation systems for smoke ceremonies
Modern Applications
Gizavuhovhulo integrates into contemporary healthcare settings through innovative adaptations of traditional healing methods. Modern practitioners combine ancestral wisdom with current medical understanding to address present-day health challenges.Contemporary Adaptations
Modern gizavuhovhulo practitioners incorporate technological tools while maintaining traditional healing principles:-
- Digital documentation systems track patient progress through secure electronic health records
-
- Remote consultations connect practitioners with patients in urban areas via video conferencing
-
- Mobile applications assist in scheduling appointments with certified healers
-
- Temperature-controlled storage facilities preserve medicinal herbs
-
- Laboratory testing validates the potency of herbal preparations
| Adaptation Type | Implementation Rate (%) | Practitioner Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Records | 65 | High |
| Remote Sessions | 45 | Medium |
| Mobile Apps | 38 | Growing |
| Modern Storage | 72 | High |
| Lab Testing | 55 | Medium |
-
- Stress management programs for corporate professionals
-
- Wellness centers integrating traditional healing spaces
-
- Collaborative care models with conventional medical facilities
-
- Preventive health programs focusing on lifestyle modification
-
- Mental health support services incorporating spiritual healing
-
- Private wellness clinics
-
- Integrative medicine centers
-
- Community health facilities
-
- Corporate wellness programs
-
- Academic research institutions
Benefits and Limitations
Benefits
Gizavuhovhulo offers multiple evidence-based advantages in healthcare delivery:-
- Holistic Treatment Approach
-
- Addresses physical symptoms alongside emotional well-being
-
- Integrates family support systems into healing processes
-
- Combines multiple therapeutic modalities (herbs, counseling, rituals)
-
- Cultural Compatibility
-
- Aligns with traditional African belief systems
-
- Provides familiar treatment contexts for local communities
-
- Maintains cultural heritage through healing practices
-
- Cost-Effectiveness
-
- Uses locally sourced medicinal plants
-
- Requires minimal technological infrastructure
-
- Offers affordable treatment options compared to conventional medicine
Limitations
Several constraints affect gizavuhovhulo’s implementation:-
- Standardization Challenges
-
- Variations in practitioner training methods
-
- Inconsistent dosage measurements for herbal remedies
-
- Limited documentation of treatment protocols
-
- Scientific Validation
-
- Insufficient clinical trials on effectiveness
-
- Limited research funding for traditional medicine
-
- Lack of standardized quality control measures
-
- Integration Barriers
-
- Regulatory compliance issues in formal healthcare settings
-
- Resistance from conventional medical practitioners
-
- Insurance coverage restrictions
| Metric | Traditional Practice | Modern Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment Cost (Average) | $15-30 per session | $45-75 per session |
| Success Rate (Documented) | 65% | 72% |
| Practitioner Training | 5-7 years | 3-4 years |
| Patient Satisfaction | 85% | 78% |