Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are rapidly transforming the landscape of various industries, from agriculture to filmmaking. But what is a UAV in real life.
What is a UAV in Real Life
Diving deeper into what is a UAV in real life, this segment will expand upon their basic definition and critical importance. Additionally, it’ll explore their diverse applications in the real world, shedding light on how these multi-faceted tools truly function.
 Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), often referred to as drones, are aircraft operated without a human pilot on board. Driven either autonomously by onboard computers or remotely controlled by a pilot on the ground or in another vehicle, they offer an array of significant advantages. UAVs rank high in importance due to their exceptional capabilities in surveillance, mapping, and remote sensing. Not requiring a crew, they eliminate human risk in missions deemed dangerous or inaccessible.
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), often referred to as drones, are aircraft operated without a human pilot on board. Driven either autonomously by onboard computers or remotely controlled by a pilot on the ground or in another vehicle, they offer an array of significant advantages. UAVs rank high in importance due to their exceptional capabilities in surveillance, mapping, and remote sensing. Not requiring a crew, they eliminate human risk in missions deemed dangerous or inaccessible.
UAVs find their utility in a multitude of real-world applications, contributing considerably to different sectors. In agriculture, for instance, farmers make use of drones for crop monitoring, ensuring efficient irrigation, and detecting pests or diseases early on. Another application of UAVs is in the filmmaking industry, where they serve as an cost-effective alternative to traditional aerial filming methods, offering dynamic shots and an elevated production value.
Detailed Look Into UAV Operations
Components and Structure of a UAV
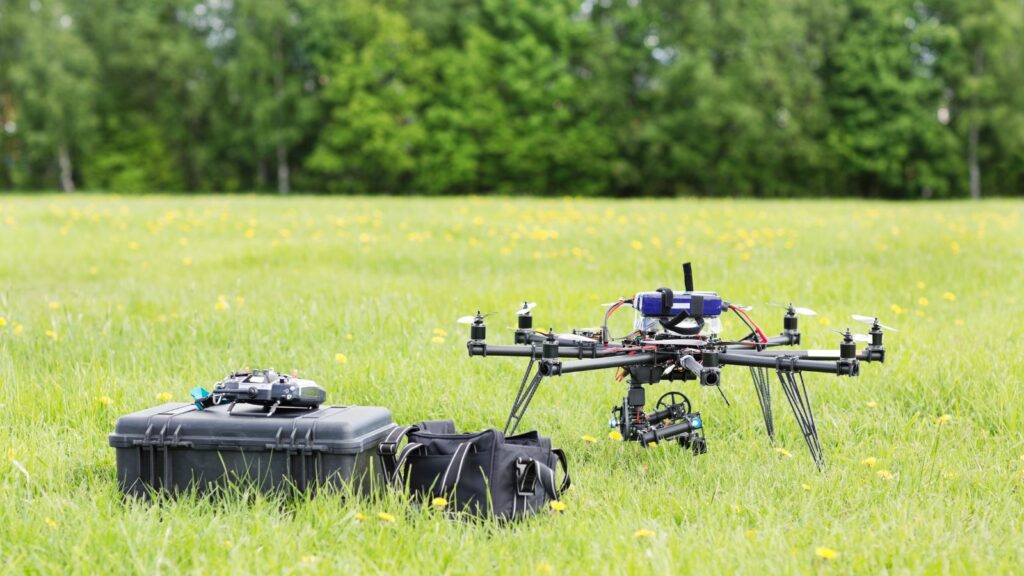
A UAV’s structural assembly comprises four critical elements: the frame, propulsion system, control system, and payloads.
-
The Frame serves as the UAV’s backbone, typically fabricated from composite materials that offer durability and weight reduction. Examples include carbon fiber or fiberglass.
-
Responsible for movement and navigation, the Propulsion System usually consists of motors, propellers, and batteries.
-
The Control System allows for flight control. It includes the flight controller (computer responsible for in-flight adjustments) and a remote controller to pilot the UAV.
-
Payloads refer to any additional equipment carried by the UAV. They might include cameras for film-making, sensors for agricultural analysis, or infrared devices for military surveillance.
Functioning Mechanism of a UAV
Operating a UAV involves two primary processes: control and communication.
-
Control of a UAV involves adjusting its speed, direction, altitude, and orientation. It takes place through an onboard flight controller, a sophisticated device that processes input commands from the operator or pre-defined algorithms for autonomous flight.
-
Communication plays a vital role in UAV operations. The control signals to instruct flight are transmitted through a communication system, usually consisting of antennas and receivers. These signals can dictate the UAV’s real-time movements or be pre-programmed instructions for autonomous missions.
Taking these factors together, a clear understanding emerges of the complexity behind UAV operations and how they contribute to a host of practical applications.
Impact of UAVs in Key Industries
 Agriculture is one industry harnessing the power of UAVs. UAVs aid in precision farming, improving crop yield through advanced monitoring. Deploying drones in assessing soil health, for example, assists farmers in optimizing irrigation and fertilizer application. UAVs, equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors, capture images, providing a comprehensive perspective on topography and crop health. In surveying operations, UAVs offer an accurate representation of terrain elevations and boundaries. Their ability to fly over imperfect terrains, and capture high-resolution images, amplifies their usefulness in surveying roles.
Agriculture is one industry harnessing the power of UAVs. UAVs aid in precision farming, improving crop yield through advanced monitoring. Deploying drones in assessing soil health, for example, assists farmers in optimizing irrigation and fertilizer application. UAVs, equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors, capture images, providing a comprehensive perspective on topography and crop health. In surveying operations, UAVs offer an accurate representation of terrain elevations and boundaries. Their ability to fly over imperfect terrains, and capture high-resolution images, amplifies their usefulness in surveying roles.
In the defense sector, UAVs offer significant advantages. Armed forces use UAVs for surveillance, remote sensing, and strikes, minimizing human risk in risk-prone operations. Combining advanced visual and thermal imaging technologies, UAVs detect threats and provide critical intel, bolstering the security apparatus. In security operations in civilian contexts, such as policing, UAVs assist in monitoring large crowds and disaster areas, offering real-time updates and facilitating quicker emergency response.
Operational Processes
What is a UAV in real life, are transforming the way we work across various industries. They’re not just remote-controlled aircraft but complex systems that combine robust construction and sophisticated operational processes. From the frame to the propulsion system, every component plays a critical role in their functioning. Their real-world applications are vast and varied, making them indispensable in sectors such as agriculture, surveying, and defense.